The black and odor of urban water bodies is one of the most severe environmental problems in China today. In April 2015, the "Water Pollution Prevention Action Plan" was released, which took the treatment of urban black and odorous water bodies as an important task. It is required that by 2020, the black and odorous water bodies in prefectural-level and above cities in the country should be controlled within 10%. It is also required that by 2030, the black and odorous water bodies in urban built-up areas should be eliminated. In May 2018, the Ecological Environmental Protection Conference made the elimination of urban black and odorous water bodies an important part of the implementation of the water pollution prevention action plan. In June 2018, the "Opinions on Comprehensively Strengthening Ecological Environmental Protection and Resolutely Fighting For Pollution Prevention and Control" was released, which made detailed provisions on the "Five Major Water-related Battles" such as the treatment of urban black and odorous water bodies.
The treatment of urban black and odorous water bodies is a long-term systematic project, which is closely related to complex factors such as unreasonable city planning, unmatched infrastructure, and imperfect supervision and management, which leads to huge challenges of the treatment of black and odorous water bodies. In February 2016, the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development and the Ministry of Environmental Protection officially released a list of black and odorous water bodies. There are as many as 2,100 black and odorous water bodies in more than 220 prefecture-level cities nationwide, and 64% of them concentrated in the southeast coastal area. Therefore, there are huge market opportunities for water treatment in China. Whether the treatment sees results depends not only on technical support, but also requires strong social capital investment. At the same time, the government's management system needs to be improved as well.
1. Basic situation of urban water environment infrastructure construction in China
Since the reform and opening up, with the acceleration of the process of urbanization in China, the proportion of urban population has increased from less than 20% in 1978 to about 60% in 2018, and the urban population has reached 800 million. The amount of sewage discharged per unit area of China's urban water system is that of European and American cities 3~4 times. Since the 1990s, the Chinese government has strongly promoted the construction of urban sewage treatment infrastructure, and investment in pollution treatment has increased year by year. By 2016, the total investment in the construction of sewage treatment projects in China’s cities had reached 148.55 billion yuan, accounting for 1.1% to 1.8% of GDP, and the average sewage treatment rate in China's cities had reached 90%, which is similar to that of European and American countries. The centralized sewage treatment rate of southeast coastal cities is over 94%, reaching the world's leading level. The density of pipe networks in urban built-up areas in China has increased from 3.17 km / km² in 1981 to 10.61 km / km² in 2016.However, the heavily polluted urban water in China remains at around 9%, and most of it is concentrated in the southeast coastal areas where economic development and sewage treatment are more advanced. The problem of urban water pollution in this context is a common problem in China and other developing countries. Its causes and countermeasures are worthy of in-depth analysis and discussion. It has an important guiding role and reference significance for the water environment governance and urban sustainable development in China and other similar countries in the world.
2. The problem of urban drainage pipe network is a challenge for the treatment of black and odorous water bodies
After years of continuous efforts, the structure of urban drainage pipe network has basically taken shape in China, but the construction planning is not systematic, the header and main pipes are relatively complete, the branch and collection pipe networks are incomplete, and the construction quality is relatively rough, which seriously affects the sewage interception and holding pipe, a large amount of pollution directly discharged into the river. The black and odorous water bodies caused by the pipe network problems in our cities can be divided into three categories.
2.1 Urban black and odorous water bodies in the background of high coverage of urban sewage pipe network.
Focusing only on the construction of sewage header and main pipes, and neglecting the construction of the collection pipe networks; emphasizing the pollution control of major rivers and not intercepting and controlling sewage according to the water system are the fundamental causes of the black and odorous water bodies in China in the background of high coverage of urban sewage pipe network.
2.1.1 Ignoring the construction of sewage collection pipe networks
The coverage rate of urban drainage pipe network has reached more than 90% in China, which is comparable to that of European and American countries and Japan, but the collection pipe network is not perfect and the density of urban drainage pipe network is far lower than that of cities in Japan and the United States and so on.
The length of the urban drainage pipe network in Japan has reached 350,000 km in 2004, and the density of the drainage pipe network is generally 20-30 km / km², in addition, the density of high-density urban areas can reach 50 km / km²; the length of the urban drainage pipes in the United States was about 1.5 million km in 2002, and the average density of urban drainage pipe network was above 15 km / km².
In the process of urban drainage network construction in China, we often focus only on the construction of header pipes and main pipes, and ignore the construction of collection pipe networks. This problem is more serious in county-level cities in China. Many pollution sources cannot be included in the sewage pipe network, so can only be discharged directly into the river channel, causing the urban river channel to be black and odorous in the background of high coverage of pipe network.
Looking back on the implementation of the first phase of the Suzhou River Water Environment Comprehensive Improvement Project in Shanghai, though the central urban sewage centralized treatment project (that is, the combined sewage treatment first-phase project and the sewage treatment second-phase project) had been completed at that time, the construction of the sewage collection pipe network not synchronized, the actual sewage collection and treatment rate is only 44%, and 56% of the sewage is directly discharged into the river without treatment. In response to this problem, the construction of the collection pipe network has been implemented, and the sewage collection rate has increased to over 90%.
2.1.2 Ignoring sewage interception and control in river networks
In the southeast coastal area where the urban water body is most polluted in China, the river network is dense, crisscross and interconnected. In the design and construction of sewage pipe network, the sewage interception of the main stream is often emphasized, and the interception of the tributaries is ignored; the sewage interception in the central urban area is ignored, and the sewage interception according to the water system is ignored, which causes the water quality of the reverberating river to affect each other, and the benefit of interception of the main stream is not obvious. For example, after the first phase of the Shanghai Confluence Sewage Project was completed in 1993, all the pollution sources directly discharged to the main stream of the Suzhou River were intercepted. However, within the confines of the six tributaries of the middle and lower reaches of the Suzhou River, there are still thousands of pollution sources not intercepted, and the amount of sewage discharged is about 300,000 m³. The pollution of the tributary has seriously affected the quality of the main stream. This is an important reason why the main stream of the Suzhou River is still black and odorous after the completion of the first phase of the combined sewage project. Subsequent development of the Suzhou River Environmental Comprehensive Improvement Project focused on the implementation of a sewage pipe network project based on the comprehensive interception of river network water systems, which effectively achieved the sewage interception and control of the entire water system, laying a solid foundation for the Suzhou River to eliminate black odor and improve water quality.
2.2 Urban water body black and odor in the background of high sewage treatment rate
According to the environmental bulletin issued by cities in China every year, the sewage treatment rate in all cities is basically above 90%, and the sewage collection and treatment rate is close to that of European and American countries, but there is a big gap in water quality. The reason is that a large amount of groundwater and rainwater are discharged into the sewage treatment plant, which artificially increases the urban sewage treatment rate. The high treatment rate number hides the truth that sewage is directly discharged without treatment, resulting in serious pollution of the river.
2.2.1 Damaged pipeline leads to large infiltration of groundwater
As of the end of 2015, the total length of China's urban drainage pipelines reached 540,000 km, of which 261,000 km of drainage pipe networks were used for more than 10 years. Due to the effects of sewage corrosion, erosion, scour, sedimentation and ground loading, serious damage of sewage pipeline is common in our cities. Laying drainage pipes below the groundwater level, groundwater enters the sewage pipe network, which squeezes the transmission capacity of sewage pipe network and reduces the influent concentration of the sewage treatment plant. There are about 1,000 in more than 4,000 sewage treatment plants in China whose COD is below 150 mg / L, and the designed sewage influent COD of the treatment plant is 350 mg / L. Comparing the two shows that the sewage treatment plant does not treat all sewage. This problem is more obvious in cities in southern China. The buried depth of sewage pipes in the south is generally 3 to 5 m, and the depth is 7 m, which is lower than the groundwater level. If the pipe network is not impermeable, groundwater will seep into the pipe network, so it is very important to solve the problem of leakage of sewage pipe network. The influent ammonia nitrogen concentration of Beijing sewage treatment plant is 38.1 mg / L, and the concentration of total nitrogen is 48.8 mg / L; the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the inlet of sewage treatment plant in southern city is 21.9-24.0 mg / L and the concentration of total nitrogen is 30.4-35.1 mg / L, accordingly, It can be deduced that the proportion of groundwater in sewage pipes in southern China can be as high as 28% ~ 40%. According to the survey, the amount of groundwater infiltration in pipelines in southern cities in China can reach 3 800 ~ 6 300 m³ / (km² · d), while that in Germany is 1 296 m³ / (km² · d), which is 3 ~ 5 times of that in Germany.
2.2.2 A large amount of rainwater illegally entered the urban sewage treatment plant
Figure 1a shows a comparison of inflow in sunny days and rainy days of a large sewage treatment plant in China from 2011 to 2018. The average annual inflow in sunny days is generally stable, the fluctuation is small, and the inter-annual change is not very obvious. However, the inflow in rainy days tends to increases year by year. The water inflow of sewage treatment plant in rainy days is significantly higher than that in sunny days. The average water inflow in rainy days exceeds that in sunny days by 14% ~ 23%, and the maximum value in rainy days reaches 1.7 ~ 2.2 times of that in sunny days during the same period.
Fig 1b compares the ammonia nitrogen concentration in the inlet water of the sewage treatment plant in sunny and rainy days. It can be seen that the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the sewage treatment plant in rainy days is significantly lower than that in the inlet water in sunny days. The annual average concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the sewage treatment plant in rainy days is 18-25 mg / L, while the annual average concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the inlet water in sunny days is 21-26 mg / L. Figure 2 shows the comparison between the inflow in sunny days and the inflow in rainy days in rainy season (May to August) in the same sewage treatment plant. It can be seen that the average difference between the inflow in rainy days and sunny days is more obvious, and the inflow in rainy days is 16% - 35% higher than that in sunny days. Rainwater enters the sewage treatment plant, increases the amount of sewage treatment, reducing the concentration of influent water, and encroaching on the transmission capacity of the sewage pipe network.
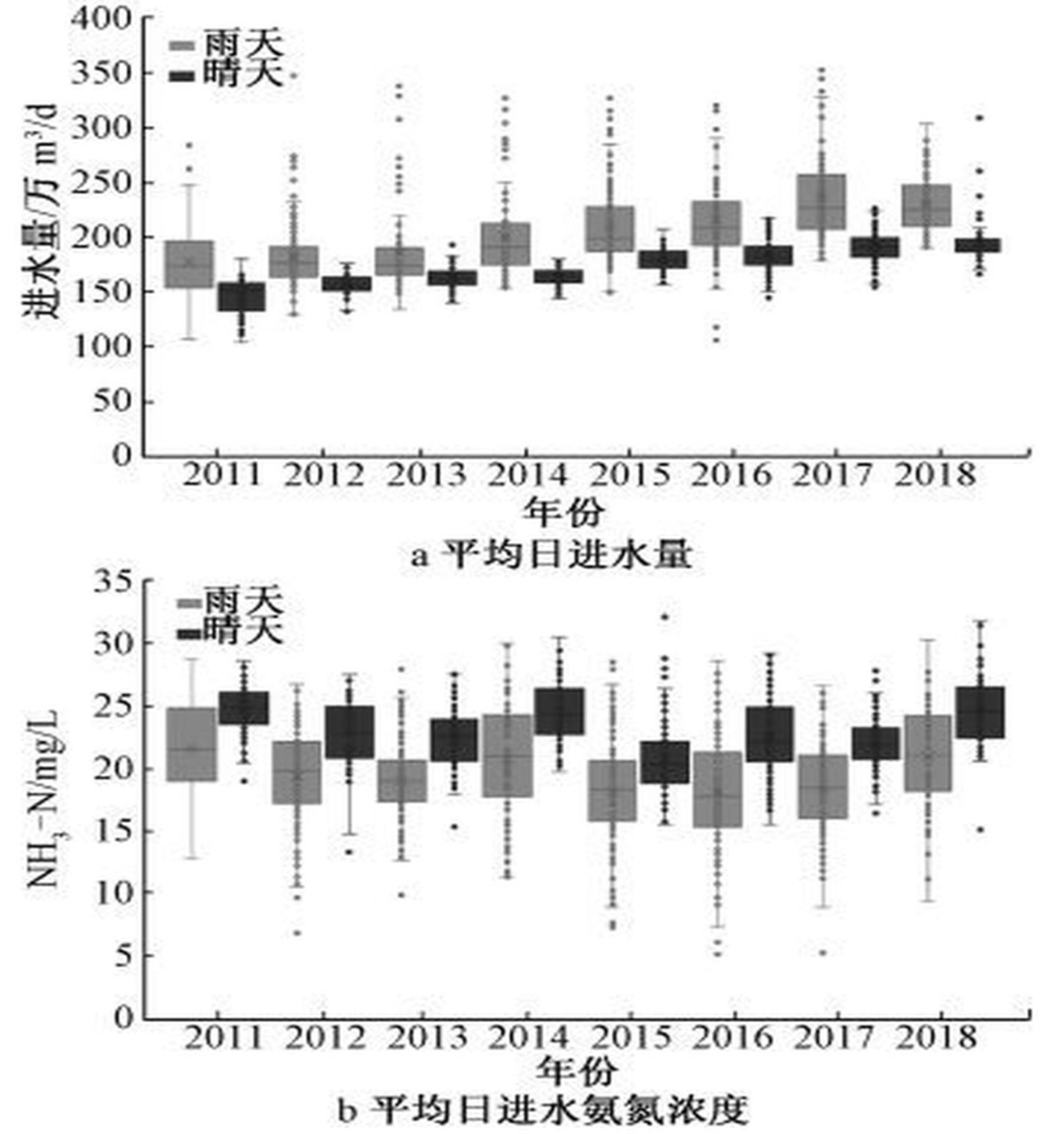
Fig1 Influent waster quantity and NH3-N of a wastewater treatment plant during wet weather and dry weather condition
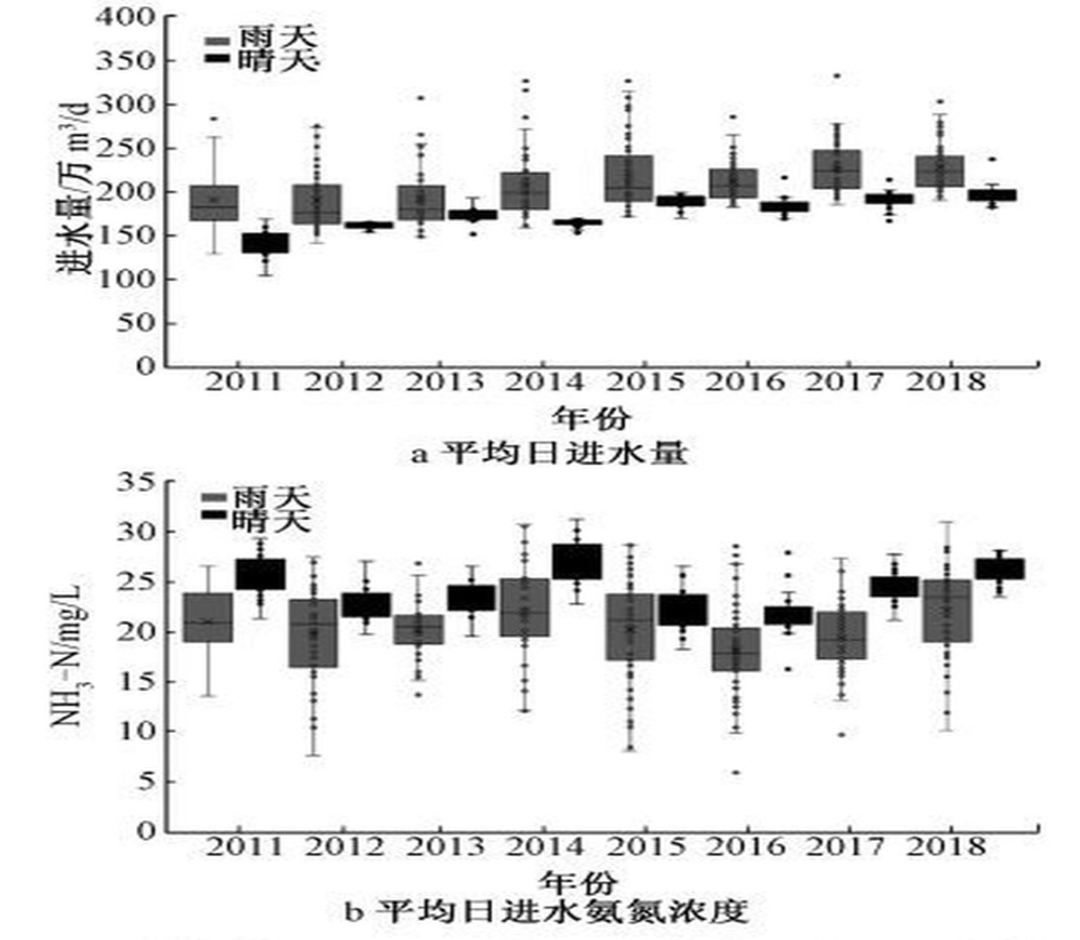
Fig2 Influent wastewater quantity and NH3-N of a wastewater treatment plant during wet weather and dry weather conditions(May, June, July and August)
This problem is even more serious in small and medium-sized cities, and events that sewage treatment plants are flooded in rainy days happens from time to time. Figure 3 is the survey results of sunny and rainy water inflows of a sewage treatment plant in a small and medium-sized city in China. The water inflows of the sewage treatment plant during rainy days are more than twice that of the dry days, so that when the rainstorm occurs, the sewage treatment plant overflows seriously, and even overflow occurs in the plant area. The illegal connection of rainwater pipes to the sewage pipe network may be due to the inadequate supervision of the construction of the pipe network. However, in some areas, in order to avoid the impact of rainy overflow pollution on the river channel, the sewage pipe network is deliberately connected.

Fig3 Relationship between influent wastewater quantity of a wastewater treatment plant and dry antecedent times
2.3 black and odorous in rainy days
With the increase in the treatment of black and odorous water bodies, many urban water bodies have eliminated the black and odor in sunny days, but it is accompanied by the black and odor of rivers in rainy days, which is particularly serious in coastal cities in southeast China. The initial rainwater discharge of the confluence system and the overflow of the rainwater pipe network of the diversion system are important causes of black and odor in urban rivers in rainy days in our country, and the most difficult problem to overcome in the treatment of black and odorous water bodies in cities in China.
2.3.1 Sewage transportation along the urban confluence system in China is heavily deposited
There are about 109,000 km of confluent pipe network in China, and the central urban area of most cities is a confluent pipe system. The scale of cities in China is large, and sewage treatment plants are usually located in the suburbs. Therefore, the transmission distance of the confluence system is relatively long, and the flow rate is slow in sunny days. The sewage pipe network has become a storage tank for particulate pollutants to some extent, leading in a low influent concentration at the terminal sewage treatment plant. According to statistical analysis, more than 70% of the sewage treatment plant’s influent COD concentration is less than 300 mg / L, and the influent COD concentration of more than 30% of sewage treatment plants is less than 200 mg / L (see Figure 4). Table 1 compares the influent water quality of typical urban sewage treatment plants in China with that of sewage plants in some other countries. It can be found that the influent NH3-N concentration of sewage treatment plants in China is comparable to the influent value of sewage treatment plants in Southern California, and the average value is even higher than that in Europe. However, the SS concentration differs by about 100 mg / L, and the average concentration of BOD and SS is 74.3% and 62.6% of the influent concentration of sewage treatment plants in these countries, indicating that nearly 1/3 of the particulate pollution is deposited along the way during the sewage transportation of the urban confluent pipe network in our country, and the settlement of the confluent system pollution along the way also reduced the influent concentration of the sewage treatment plant.
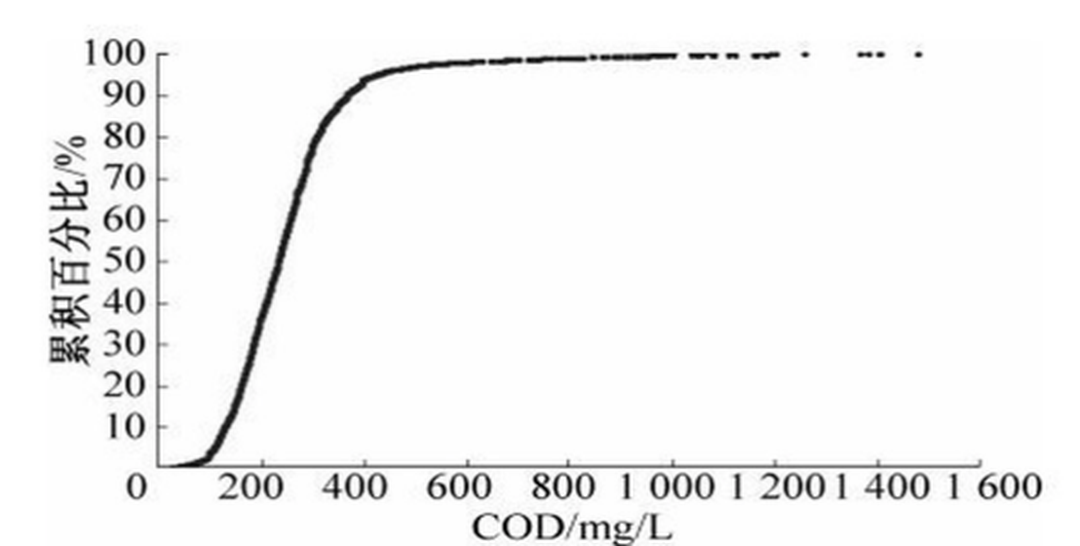
Fig4 Cumulative proportion of influent COD concentration of wastewater treatment plants in China

2.3.2Serious rain and sewage mixed connection in urban separation system in China
The construction of sewage pipeline networks in cities in China has lagged behind urban development for more than 20 years. In the case of urban drainage backbone pipeline networks that have not been popularized first, in order to solve the sewage discharge in these areas, temporary measures such as rain and sewage mixing have been adopted to connect the sewage to the urban rainwater pipe network, and temporarily met the sewage discharge demand. Due to the lack of renovation in a long period of time, the temporary measures have become permanent measures. Up to now, a large amount of pollution is still directly discharged into the rainwater pipes, and the mixing of rain and pollution is still relatively common.
According to the survey results of some cities in southern China, the sewage discharged into the rainwater pipe network overflows when it rains, and the COD discharge is as high as 800 ~ 1 100 mg / L, which causes the river to be black and odorous in rainy days. China's National Water Pollution Control and Governance Science and Technology Major Special Project has used a city as a model to carry out a study on the identification and transformation of rainwater and sewage mixing in a separation system. Figure 5 shows a survey result of the rainwater and sewage mixing situation of 23 separation systems in eastern cities in China. The average amount of sewage illegally discharged into the rainwater pipeline accounts for about 26.2% of the total sewage in the service area, up to 70%.

Fig5 Proportion of inappropriate sewage entry in separate systems
2.3.3 The rainwater and sewage mixing of the diversion system and the deposition of the confluence system lead to black and odorous water in rainy days
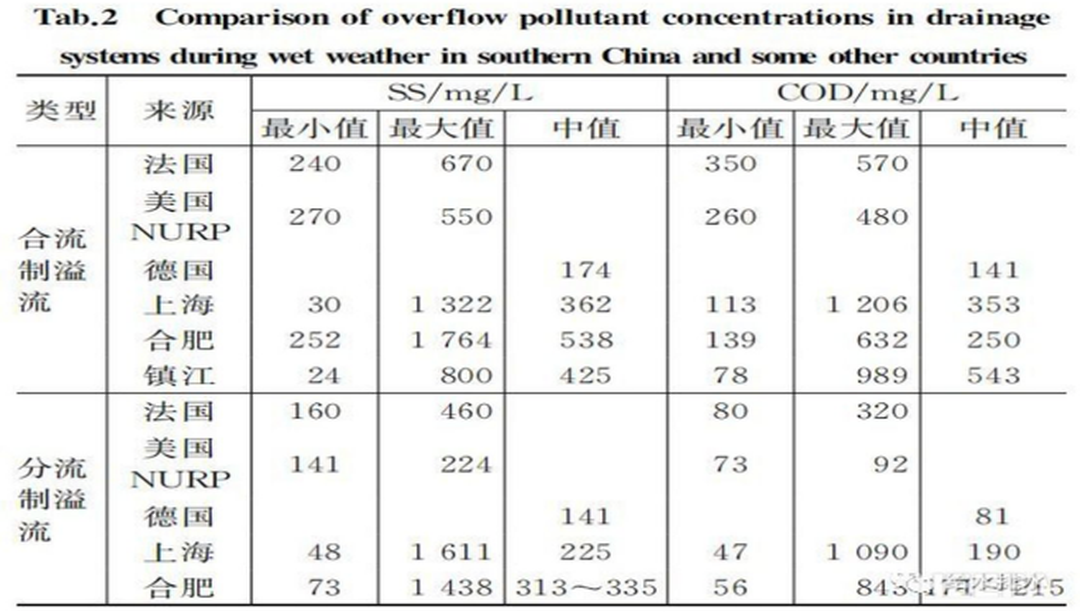
The main cause of black and odor of urban water bodies in rainy days in our country is rainwater overflow pollution in the separate system and the confluence system. Table 2 shows the concentration of rainy overflow pollution in some cities in southern China, France, Germany and the United States. It can be seen that in the south of China, when the confluence system discharges in rainy days, the COD is as high as 1 200 mg / L, and the average value is as high as 540 mg / L. The overflow pollution concentration of the separate system, whether it is the maximum concentration or the median value, is more serious than the countries listed in the table, and even more than 2 times higher.
3. Technology demand and market outlook
With the rapid development of urbanization in China, the urbanization rate has increased from 36.22% in 2000 to 57.35% in 2016, but infrastructure construction such as underground pipeline networks has not kept up. For a long time, China's urban pipeline network construction investment is insufficient, and the drainage pipeline network system is seriously damaged. With the exposure of the persistent problems in the treatment of urban black and odorous water bodies, the public and even decision-makers finally realized the reality that the lagging construction of the urban drainage system is becoming a stumbling block to improve the quality of urban water environment in China, a barrier that cannot be bypassed, or a problem that must be faced sooner or later.
3.1 Technical requirements
Due to dense population, heavy traffic, and numerous tall buildings, it is very difficult to solve the problems of urban pipeline network in China. There is a huge technical demand for underground survey, underground repair, and underground construction. It is more difficult to repair a broken pipe network in a high-density urban area than to build a new pipe network. This is the result of China's long-term development idea of "emphasis on the ground and light under the ground".
(1) Reconstruction of rain and pollution mixing. This is the key to solving the problem of black and odor in urban water bodies in China, and it is a prerequisite to carry out the transformation to find out the mixed rain and sewage in the underground pipe network. There is an urgent need to develop robots for tracing and tracking mixed pollution sources and robots for detecting and diagnosing the underground pipeline network, and to determine targeted engineering technologies. It is very difficult to carry out ground excavation and rain-sewage mixed transformation in highly modern urban areas. At present, the measures taken by cities in our country are initial rainwater storage and dry-flow sewage interception. The solution to the problem of black and odor in rainy days is very limited. The rapid purification of the overflow pollution terminal and the development of interception devices are very important. It is necessary to realize automatic online storage of the drainage pipe network.
(2) Pipeline repair. Due to the effects of corrosion, erosion, scour, sedimentation and ground load of sewage, the drainage pipe network has defects of varying degrees such as damage, staggering, water seepage, water leakage, siltation and blockage. The development of underground pipeline network detection instruments and equipment is very urgent. The demand for underground pipeline network diagnosis and repair technology has greatly increased, and the construction of trenchless pipeline network and water repair technology is urgently needed to be introduced. At present, the trenchless repair technologies currently being applied in the domestic market are the spotless in-situ curing method, the stainless steel sleeve method and other local trenchless repair technologies and the ultraviolet in-situ curing method, the segment lining, the short tube lining, and the expansion tube method. The relevant environmental protection industry and engineering construction market will also usher in a round of outbreaks.
(3) Cleaning up sediment. Sediment cleaning of long-distance transported confluence pipelines is an effective measure to control overflow pollution. At present, our country basically adopts artificial dredging with low efficiency. Therefore, there is a large demand for technical methods such as pipe deposition prevention technology, mechanical dredging and hydraulic automatic flushing. Demand for the harmless and resource-removing treatment and disposal technology for dredging sludge is very urgent. With the emphasis on pipeline deposition pollution, related devices, structural design, construction and construction management will become hot spots.
(4) Low-impact development. Through the blocking, interception, storage, and infiltration of green infrastructure, rainfall runoff can be effectively reduced, thereby reducing the overflow pollution of the confluent pipe network and the separate rain pipe. Studies have shown that green infrastructure can effectively reduce the frequency of overflow and slow down the scour of sediments, especially in the case of light rain, the effect is very obvious. The coupling design and optimal management of the traditional gray drainage facilities and green drainage facilities will become the mainstream technology to improve the drainage capacity and reduce runoff pollution.
(5) Smart water affairs. Most cities in China, especially small and medium-sized cities, have low levels of operation and management of drainage networks. Many cities still use the traditional management model that relies on paper drawings and even the memory and experience of old workers. Although with the popularization and development of computer technology, many cities have carried out information processing of drainage network data, but the degree of informatization and specialization is relatively low, which cannot reflect the systematic nature of the drainage network. In addition, some cities have adopted a GIS-based management system to realize the map display and query functions of the geographical characteristics of the urban drainage pipeline network, but they cannot achieve network analysis, dynamic simulation and optimization analysis of the drainage pipeline network, and cannot provide scientific decision support for the safe operation of the urban drainage network. Sensor-based pipe network, river network operation monitoring, as well as integrated mathematical model prediction, real-time data analysis, expert case database query and inference smart water platform development, also has great room for development.
3.2 Market Outlook
In April 2015, the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Environmental Protection issued the “Implementation Opinions on Promoting Cooperation between the Government and Social Capital in the Field of Water Pollution Prevention”, proposing to promote the PPP model in the field of water pollution prevention, improve the investment and financing environment, guide social capital to actively participate in and increase investment, and improve the capacity of water pollution treatment. The treatment of black and odorous water in China is changing from a potential market to a real market. The Chinese government implements pay-as-you-go and regularly evaluates the investment governance and operation effects of social capital during the operation of PPP projects for the treatment of black and odorous water bodies, and the evaluation results are used as the basis for payment of project operation service fees. The participation of social capital in the treatment of urban black and odorous water bodies can not only solve the problem of short-term centralized investment of funds by the government, but also transform the environmental management project into a contract that is pay-for-effect and easy to manage. In this way, through multi-party collaboration, short-term remediation and long-term maintenance are combined to promote the treatment of black and odorous water bodies and ensure the stable operation of the treatment plan. At present, the river water environment management PPP project has developed to a certain scale. As of July 2018, the Ministry of Finance has 131 PPP projects for river water environment management, with a total investment of 225.918 billion yuan.
At present, the PPP project of urban water environment treatment in China does not include the repair and improvement of the existing pipeline network basically, which is also the fundamental reason for the "repetitive treatment and repeated treatment" of the existing urban black and odorous water treatment PPP project. PPP projects can only see long-term effects if they include the improvement and restoration of the drainage network. However, there is a large gap between the data of urban pipeline network and the actual situation in China. The drainage pipeline network generally has problems such as groundwater infiltration, foreign body penetration, pipeline misconnection, pipeline siltation, and pipeline network rupture. Most domestic operating companies participating in PPP projects are comprehensive environmental protection service companies or cross-borders with strong capital strength, not many companies specializing in the treatment of black and odorous water bodies, lacking the professional skills of pipeline network repair, facing the difficult problem of repairing and improving high-density urban drainage network, they are powerless both in technology and engineering construction.
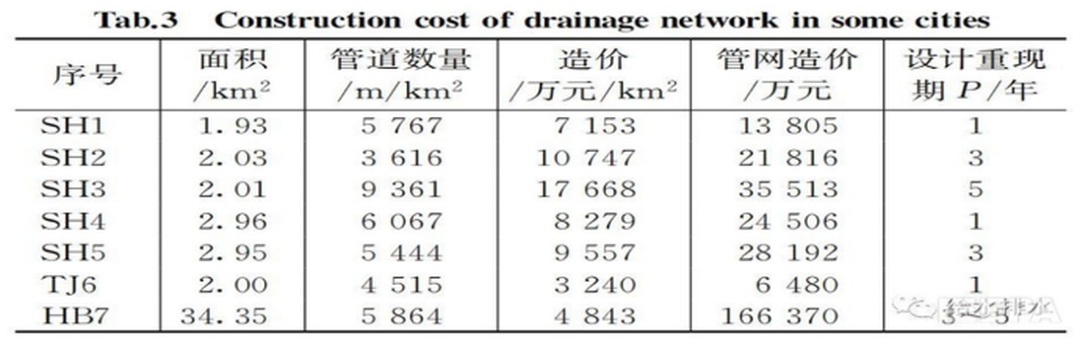
According to Figure 6, the urban sewage pipe network in China is only 2/3 of the water supply pipe network, which means that there is a gap of about 1/3 of the urban sewage collection pipe network. Table 3 shows an analysis of the cost of the drainage system undertaken by a design institute in China. The construction cost of the drainage pipe network is 720 to 18.99 million yuan / km². Based on this calculation and analysis, the urban sewage collection pipe network in China construction requires an investment of nearly one trillion yuan. According to the survey of the drainage pipeline network that has been carried out in China, the damage rate of the underground pipeline network built in large cities is nearly 30%, and the situation in small and medium-sized cities may be more serious. According to this estimate, the investment in urban pipeline network repair projects in China will exceed several trillion yuan. According to public information, during the "Thirteenth Five-Year Plan" period, the sewage pipeline network construction and renovation investment in China will exceed 300 billion yuan. At present, the topic of urban pipe network in China has obviously increased, and many enterprises related to the pipe network have performed well. The urban sewage pipe network, which was not valued in the past, has gradually ushered in the industry.
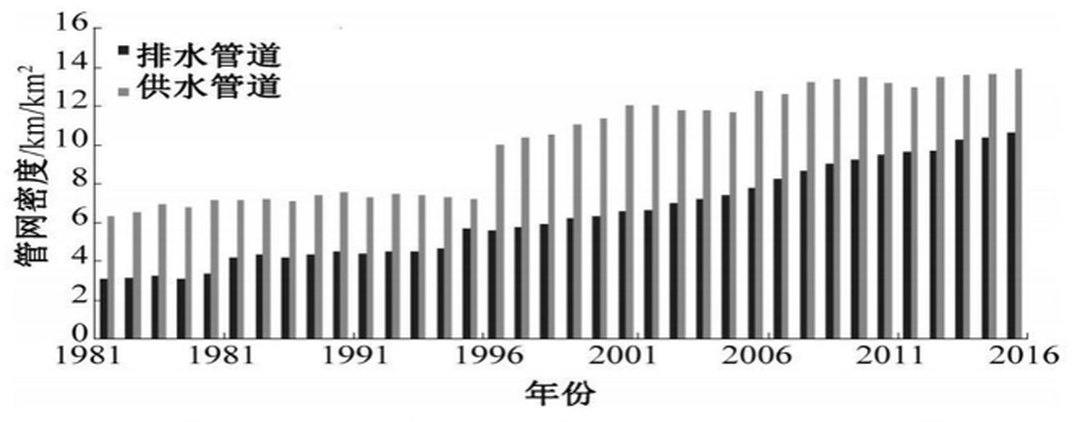
Fig6 Comparison of density of urban water supply network and drainage network in China
At present, the operation of urban drainage pipeline network in China is basically operated by subsidiaries of urban investment and construction groups under governments at all levels, and the level of professional operation and maintenance is not high. The operation and management of the urban drainage pipeline network should also explore new operation modes, introduce professional operation and management teams, adopt new operation modes such as contract management or PPP, and provide the government with management services covering four stages of "investigation, diagnosis, governance and maintenance" by using the professional talents, new technology and new technology of the professional team diagnosis, treatment and maintenance", take charge of the whole process management of the urban drainage pipe network operation and solve the existing problems of the drainage pipe network. The government implements the assessment of the urban drainage pipe network operation and management results, and realizes the transformation of the management mode from "focusing on construction" to "supervision and management", and the corresponding market costs are estimated to exceed hundreds of billions of yuan.
The improvement of urban drainage network repair and subsequent management combined with PPP project will fundamentally change the current status of the urban drainage pipe network, help to achieve the goal of urban black and odorous water treatment, and promote the vigorous development of the environmental protection market. New technology, new devices and new management models will give birth to a group of enterprises specializing in the repair and management of pipeline networks, and the huge market in China will bring huge benefits to them. 2018 ~ 2020 will be a critical period for the development of black and odorous water treatment market in China. The market and policy integration will be further strengthened, and the service model will be further innovative. Based on the treatment technology, a new service model that opens up the industry chain will become an important direction for the future market.
4. Summary
The improvement and repair of urban drainage pipe network is the key point of urban black and odorous water body treatment. New technologies and new products are urgently needed, including rainwater pollution identification, rapid treatment of overflow pollution, drainage pipe network water restoration, trenchless construction, green drainage facilities and other technologies. Smart water services, biotechnology, green technology, and the integration of new materials are the key technical means for the treatment of black and odorous rivers in cities with high pipe network coverage in China. To improve the service quality and efficiency of the urban drainage pipe network, it is necessary not only to accelerate the full coverage of the urban drainage pipe network, but also to ensure the healthy operation of the drainage pipe network, so as to realize the full collection and transmission of sewage by urban drainage network.
The treatment of black and odorous water in our country has reached the critical moment of "resumption" in the medium term. How to take the road in the next 3 to 5 years is a topic that the government, enterprises and the public need to face together. Moreover, in addition to 295 prefecture-level cities, there are county-level cities, county towns, and organized towns where the pressure of black and odorous water treatment cannot be underestimated. How to consolidate the effect of the already cured river and ensure that it does not rebound is also a problem to be faced in the future.
The key to fighting the urban black and odorous water bodies is to promote the construction of urban environmental infrastructure and urge local governments to establish a long-term mechanism to ensure the long-term development of black and odorous water bodies. The experience of black and odorous water treatment in China and the repairing technology and management model of urban drainage pipe networks
have guidance and reference significance for the water environment management in developing countries.








